When it comes to homebrewing, achieving the perfect balance of flavors is key. One essential tool for brewers is the BU:GU ratio, which helps balance bitterness and sweetness in your beer. Let's dive into what this ratio is and how you can use it to enhance your brewing recipes and processes.
What is the BU:GU Ratio?
BU stands for Bittering Units, also known as International Bittering Units (IBUs). This measures the bitterness of your beer. Bitterness is achieved in a beer by adding hops during the boiling process.
GU stands for Gravity Units, which indicates the amount of sugar in the unfermented wort. This is typically expressed as a specific gravity figure like 1.050. For the BU:GU ratio, we use the numbers to the right of the decimal place. For example, a gravity reading of 1.050 translates to 50 gravity units (GU).
 |
| Hops are added during the boiling of wort to impart bitterness |
Calculating the BU:GU Ratio
To calculate the BU:GU ratio, divide the IBUs by the gravity units. Here are a couple of examples:
Example 1: A beer with 30 IBUs and a gravity of 1.030 would have a BU:GU ratio of 1 (30/30).
Example 2: A beer with 15 IBUs and a gravity of 1.045 would have a BU:GU ratio of 0.33 (15/45).
Using Brewing Software
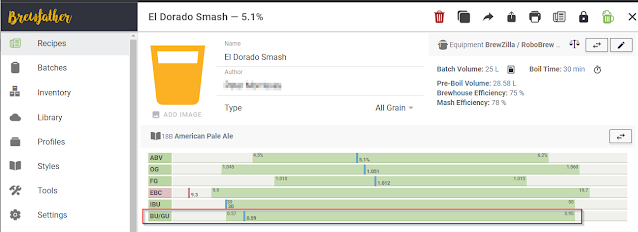
Most popular brewing software, such as Brewfather, automatically calculates the BU:GU ratio for your recipes and provides a target range based on the beer style you're making. For instance, Brewfather might suggest a BU:GU ratio range of 0.57 to 0.95 for a particular style, and your recipe might currently be at 0.59 - as per the example below;
Importance of the BU:GU Ratio
The BU:GU ratio is crucial for balancing bitterness and sweetness in your beer. While the suggested figures are guidelines rather than strict rules, they help ensure your beer's flavor profile is balanced and appropriate for the style you're aiming for.
Falling outside of the recommended ratio could lead to a beer that is too sweet, or too bitter for the style.
Example Ranges for Different Beer Styles
Understanding the BU:GU ratio for various beer styles can help you achieve the perfect balance of flavors. Here are some example ranges for different types of beers:
Wheat Beers: 0.25 - 0.35
Pale Ales: 0.4 - 0.6
Amber Ales: 0.5 - 0.7
Brown Ales: 0.6 - 0.8
Porters: 0.6 - 0.9
Stouts: 0.7 - 1.0
IPAs: 1.0 and greater
Double IPAs: 1.2 and greater
Barleywines: 0.8 - 1.2
Saisons: 0.4 - 0.6
Belgian Tripels: 0.5 - 0.8
These ranges are guidelines to help you balance the bitterness and sweetness in your beer, ensuring a well-rounded flavor profile that suits the style you're aiming for. Brewers can of course experiment within these ranges to find the perfect balance for their own taste preferences
Additional Tips for Homebrewers
Experiment with Ratios
Don't be afraid to experiment with different BU:GU ratios to find what works best for your taste preferences.
Consider Other Factors
Remember that other factors, such as the final gravity, malt profile, and hop varieties, also influence the overall flavor and balance of your beer123.
By understanding and utilizing the BU:GU ratio, you can create well-balanced and flavorful beers that are sure to impress.


No comments:
Post a Comment